Dental aesthetics
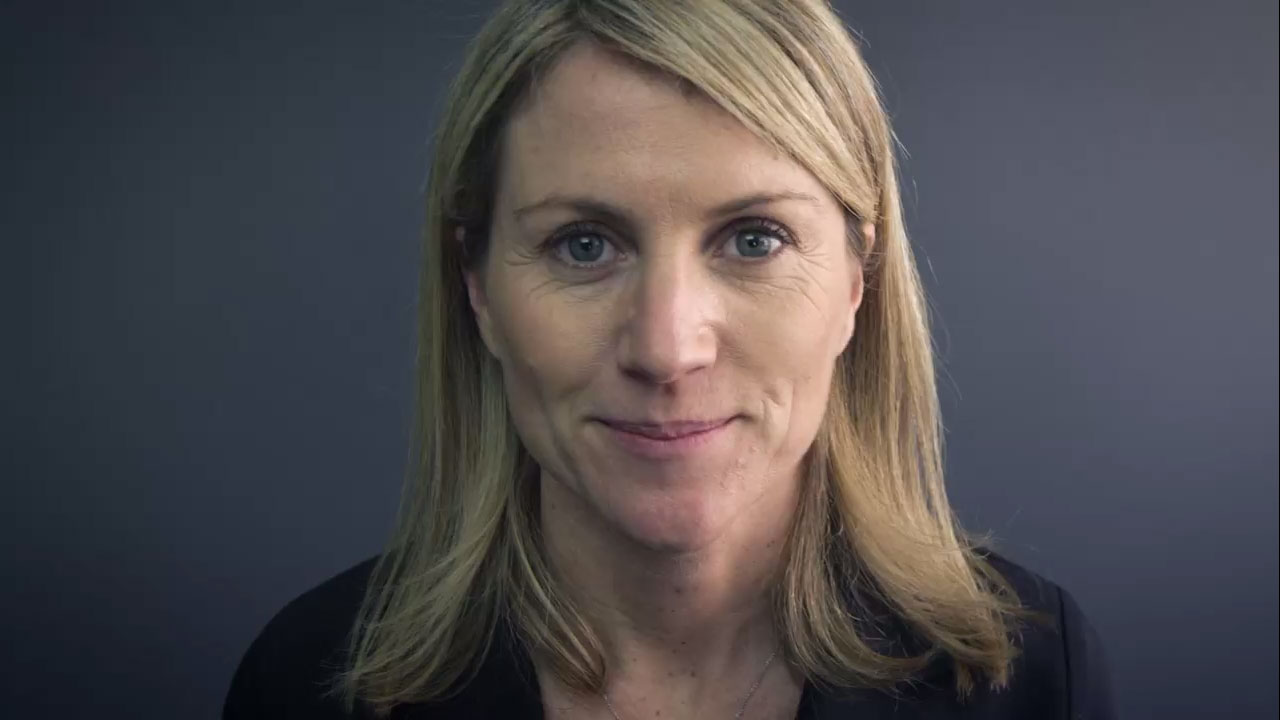
One of the fundamental aesthetics aspects of a face is the smile. During a simple chat the look of our interlocutor passes quickly and unconsciously from our eyes to our mouth. It is clear how our smile and our teeth become our business card. The color and shape of the teeth, the texture and the line of the lips are essential details that can improve a person's appearance and rejuvenate it.

Often improving the appearance of the teeth also improves the support of the lips giving an excellent overall effect. A smiling face is perceived as a healthy and beautiful face. In our practice, the aesthetic cases are analyzed in detail and individualized according to the physiognomic characteristics and personal needs of the patient. The treatment plan in an aesthetic rehabilitation is very important. We collect a series of data through photos and impressions that allow us to utilise a procedure called Smile Design, showing the patient a preview of what the final result will be both on the computer and physically on the patient with test temporary prosthetics called Mock up.
The patient can then decide if the shape and color of the restorations satisfy him/her or not.
Veneers
The first ceramic veneers were used at the end of the last century to improve the smile of Hollywood actors. The construction and cementation techniques were primitive and this procedure fell into disuse in the 80s, when the advent of more sofisticated and tested adhesive methods made ceramic restorations safe and durable.
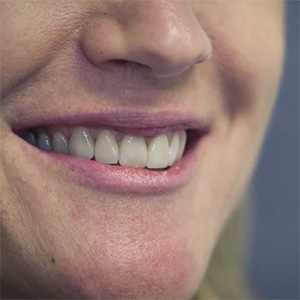
This treatment essentially consists in replacing the visible portion of dental enamel with a ceramic restoration that is adhesively cemented to the tooth surface (this step is very important as the veneers have no retention on the tooth) and it acquires a very similar optical, mechanical and biological properties to those of natural enamel.
The main indication for this treatment is that of incisors elements that require changes in shape, color and position. Also in this case a thorough examination is necessary to decide if the ceramic veneers represent the best aesthetic solution for the patient.
Metalfree crowns
When the changes to be made on the tooth, to improve aesthetics, are very important it is necessary to use full crowns. The all-ceramic crowns are metal-free crowns and have optical and mechanical properties very similar to natural teeth.
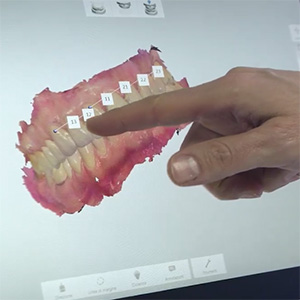
The absence of metal also makes it possible to be more conservative when preparing the tooth and not having to hide any metal edges, placeing the crown margin at the level of the gingival margin or even out of the margin itself. This procedure allows to limit the traum on the gingival tissues facilitating the oral hygiene and therefore the periodontal health.
This ceramic crowns can be made mainly of 2 types of material: Lithium Disilicate and Zirconia. It is the Dentist who chooses the material according to the clinical situation, differentiating if the teeth to cover are in the anterior or posterior area or according to the discromia of the tooth and the amount of dental tissue left. Unfortunately, the counterfeiting of materials is a phenomenon that afflicts dentistry as well and it is always better to rely on scrupulous professionals being wary of treatment plans (especially aesthetic ones) with too low cost estimates. Like the veneers, the full ceramic crowns are adhesively cemented onto the tooth surface. This adhesive bond reinforces the mechanical strength of the crowns, reducing the risk of fracture. Adhesive cementation is one of the most delicate moments of aesthetic treatment and must be performed following a precise protocol that depends on the material used for the restoration.
Fillings and inlays
Although caries today tends to be no longer a common pathology, conservative treatments remain the most common aesthetic rehabilitations both for the treatment of primary caries, fractures or the replacement of old fillings that are no longer aesthetic or functional.
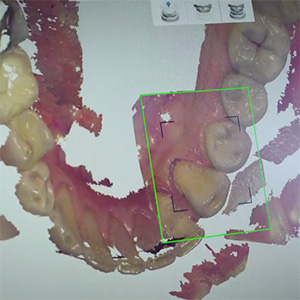
The mimetic materials available for the restoration are the composite resin for the decayed teeth and cermics for more extensive restorations (inlays and onlays). The composite is a resinous material and is normally used to fill the tooth cavity directly after removing the caries.
Ceramic or even composite inlays are made indirectly. After the removal of the carious tissue, the tooth cavity is finished and an impression is taken. From the impression we obtain a precise model of the dental arch on which the dental technician will realize the inlay that will be cemented adhesively on the tooth.
The indications for the use of a direct or indirect technique depend on the clinical situation and the quantity of healthy residual tooth.
Prosthesis
The main purpose of prosthesis is to restore the shape, function and aesthetics of the severely compromised teeth and to make the crowns that will replace the teeth on implants.
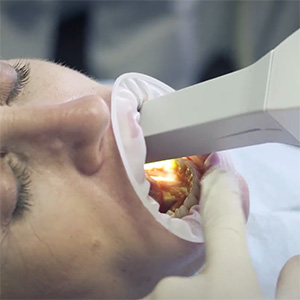
Prosthetic rehabilitation must follow precise protocols that pass through the collection of patient data (study models, radiographs, photos and periodontal health status) to formulate a correct diagnosis and a treatment plan.
Even if it is a single tooth, the use of temporaries is fundamental to the rehabilitation. This also to respect the biological healing times for the maturation of the tissues surrounding the teeth and the execution of all the structural and aesthetic tests that will lead to the final product.
Our practice is able to offer the best customized prosthetic treatment for the patient based on aesthetic, functional and economic needs. New technologies and procedures reduce the time and cost of treatment. In our clinic it is available the Trios® introral scanner, probably the most accurate on the market. This device allows to make an optical impression of the dental arches without using the annoying impression materials. The three-dimensional file obtained is sent directly to the laboratory which in turn will work it digitally to make the final prosthesis to the patient.
